カルマンフィルター (Kalman filter) を試す
2023年 05月 23日 火曜日
これは2023/05/23のMK社内LTで発表した内容です。
カルマンフィルターとは?1
- 誤差のある観測値を用いて、ある動的システムの状態を推定るためのフィルターである
実用例1
- 現在・未来・過去における対象物体の位置推定
- 自動車の位置推定
歴史1
- NASAのアポロ計画でロケットの軌道推定などに使われた歴史がある
カルマンフィルターを使う理由?
- 観測でデータを収集する
- 観測の不確かさがある
- 平滑(へいかつ)化するため
前提条件
- 線形離散(せんけいりさん)時間状態空間モデル
コンセプト
- より精確な値を得るために、測定値と予測値の重み(カルマンゲイン)を計算する
アルゴリズム2
数式
- 予測
- 状態方程式:
x(n+1, n) = Fx(n, n) + Gu(n) - 共分散遷移式:
P(n+1, n) = FP(n, n)F^T + Q
- 状態方程式:
- 更新
- カルマンゲイン:
K(n) = P(n, n−1)H^T / (HP(n, n−1)H^T+R(n) - 状態更新式:
x(n, n) = x(n, n−1) + K(n)[Z(n) − Hx(n, n−1)] - 共分散更新式:
P(n,n) = [I − K(n)H]P(n, n−1)
- カルマンゲイン:
記号
- x: 状態ベクトル
- F: システム行列
- G: 入力係数行列
- u: 入力変数
- P: 推定の不確かさ
- Q: プロセス雑音の不確かさ
- K: カルマンゲイン
- R: 観測の不確かさ
- z: 観測ベクトル
- I: 単位行列
流れ
- 初期化
- 予測1回目
- 更新1回目
- 予測2回目
- 更新2回目
- …
- 予測n回目
- 更新n回目
- …
実装
- 1次元カルマンフィルタ
class KalmanFilterOneDimension:
# https://www.kalmanfilter.net/multiSummary.html
def __init__(self, initial_value, state_transition_matrix=1.0,
observation_matrix=1.0, process_noise_matrix=0.05,
measurement_noise=0.1, estimated_error=0.1,
control_matrix=0.0, measurable_input=0.0):
self.F = state_transition_matrix # state transition matrix
self.H = observation_matrix # observation matrix
# variance state transition matrix (process noise matrix)
self.Q = process_noise_matrix
# measurement noise covariance matrix (variance observation matrix)
self.R = measurement_noise
# squared uncertainty of an estimate (covariance matrix)
self.P = estimated_error ** 2
self.G = control_matrix # control matrix
self.U = measurable_input # measurable (deterministic) input
# Skip process noise, i.e. an unmeasurable input that affects the state because it does not typically appear directly in the equations of interest
# Instead, this term is used to model the uncertainty in the covariance extrapolation equation
self.kalman_gain = 0.0
self.predicted_value = 0.0
self.estimated_value = initial_value
def __predict(self):
# https://www.kalmanfilter.net/stateextrap.html
self.predicted_value = self.F * self.estimated_value + self.G * self.U
# https://www.kalmanfilter.net/covextrap.html
self.P = self.F * self.P * self.F + self.Q
def __update(self, measurement):
# https://www.kalmanfilter.net/kalmanGain.html
self.kalman_gain = self.P * self.H / \
(self.H * self.P * self.H + self.R)
# https://www.kalmanfilter.net/stateUpdate.html
self.estimated_value = self.predicted_value + self.kalman_gain * \
(measurement - self.H * self.predicted_value)
# https://www.kalmanfilter.net/simpCovUpdate.html
self.P = (1 - self.kalman_gain * self.H) * self.P
def execute(self, measurement):
self.__predict()
self.__update(measurement)
return self.estimated_value- 使い方
# Set Kalman filter parameters
# consider the current state as the next state (no change)
state_transition_matrix = 1.0
observation_matrix = 1.0 # consider no scaling between the state and the measurement
process_noise_matrix = 0.05 # guessing value
measurement_noise = 0.5 # guessing value
estimated_error = 0.0 # according to the initialization estimate error
control_matrix = 0.0 # no control input
measurable_input = 0.0 # no measurable input
# Initialize Kalman filter
speed_kf = KalmanFilterOneDimension(speed_measure[0], state_transition_matrix,
observation_matrix, process_noise_matrix,
measurement_noise, estimated_error,
control_matrix, measurable_input)
# Execute Kalman filter
for i in range(len(speed_measure)):
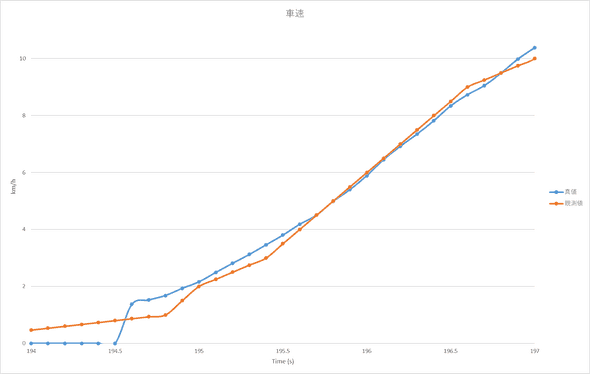
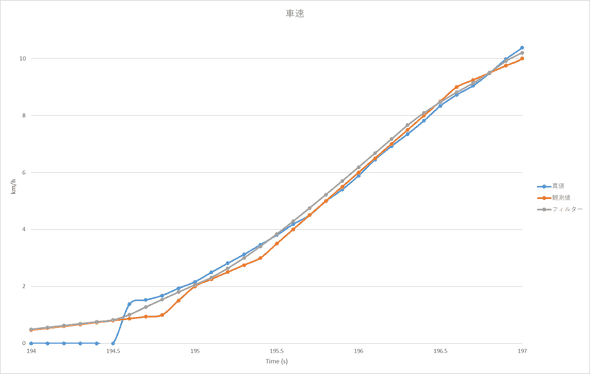
speed_estimate.append(speed_kf.execute(speed_measure[i]))デモ
References
この記事をシェア